In human history, people have never stopped learning. While humans exploring the knowledge, they are also exploring the possibility of the different learning methods and learning theory. Students now have more chances to take different formats of learning based on their choices. No matter they choose the traditional instructor-centred face-to-face learning or they choose distribution open student-centred online learning, the outcome and objective are the same: to learn knowledge. There are lots of way of gain knowledge, some student likes to read from books, some student like to learn from their experience. Consider the COVID-19 situation, when students are all staying at home, how can students learn more efficient? How student can experience better when they learn while they all at home become a hot topic during this special time. The introduction of Extended Reality technology in distribution and Open learning helps enhance students’ experience in learning. Although this technology is still in development and gowning but can have merit to support distributed and open learning in a meaningful way.
Extended Reality Technology
Most people might familiar with Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) from movies and news. But what is the Extended Reality? Extended reality (XR) is a combination of all the immersive technologies. Currently, there are three main components of XR: Virtual, Augmented and Mixed Reality. XR can also include future realities that technology can bring to cover the full aspect of real and virtual environments.
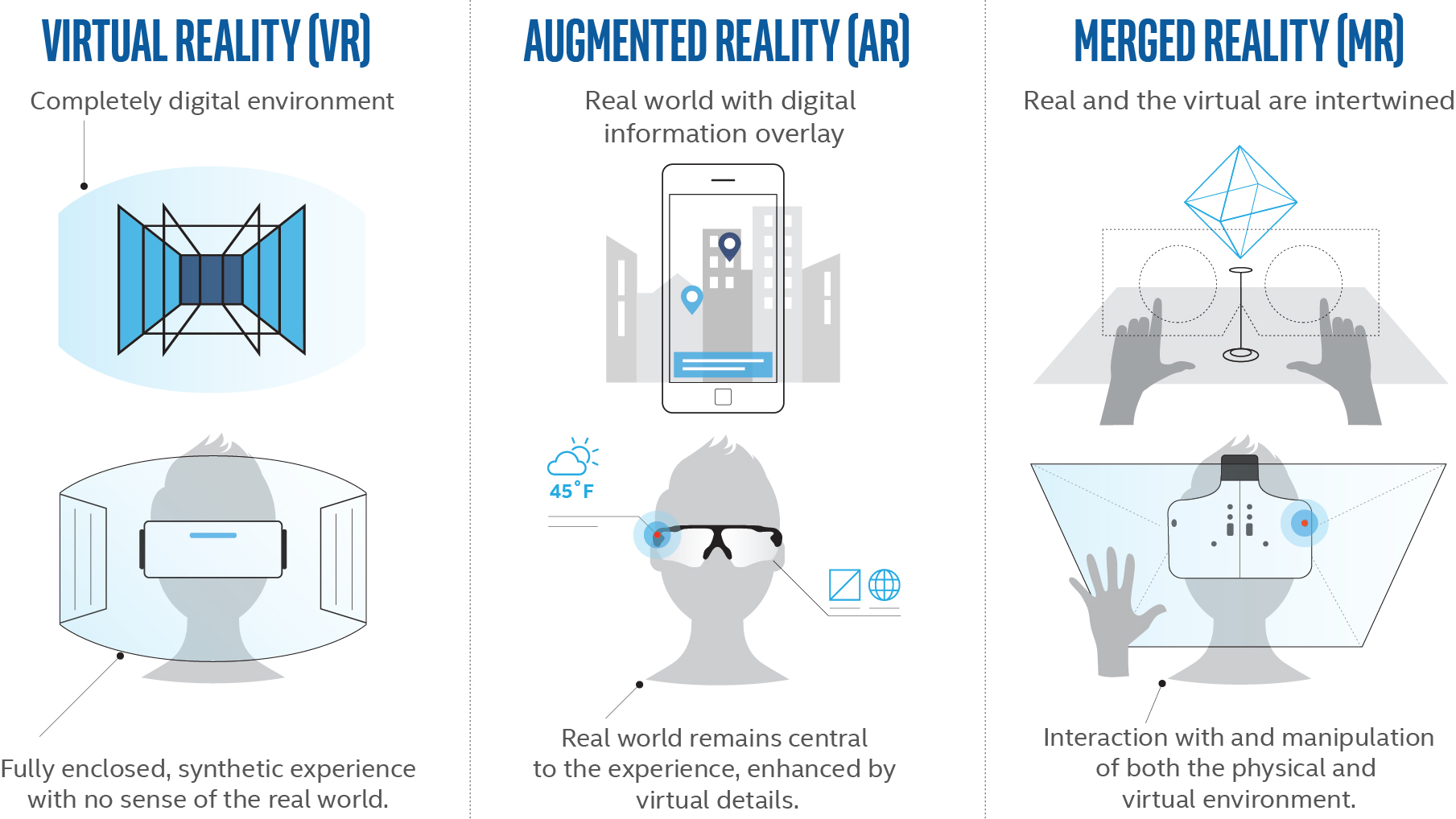
Virtual Reality (VR): usually refers to technology that provides users with a simulated experience of realistic sounds and images by using a VR headset or head-mounted display (Marr, 2019). For example, users can experience walking on the moon.
Augmented Reality (AR): is a new technology that focuses on users’ “sight” where user can see the computer-generated information in a real word such as “Pokémon GO” (Najjar, 2020)
Mixed/Merged Reality (MR): as what people can tell from the name; it is a technology what mixed between VR and AR. “It blends real and virtual worlds to create complex environments where physical and digital elements can interact in real-time” (Marr, 2019).
Extended Reality: The Top Five Things You Need to Know
By involve XR in education, it brings opportunities for students to have immersive learning experiences in their learning. By using XR, students are no longer limited by time, space and environment. XR improved students learning opportunities in a broad range of needs. However, as a technology that is still in development and not in widely use for students yet, will this tool really fit students’ needs in content delivery, collaboration, assessment? The SECTIONS model developed by Tony Bates is a framework that can be used for instructors to assess this technology.
SECTIONS model
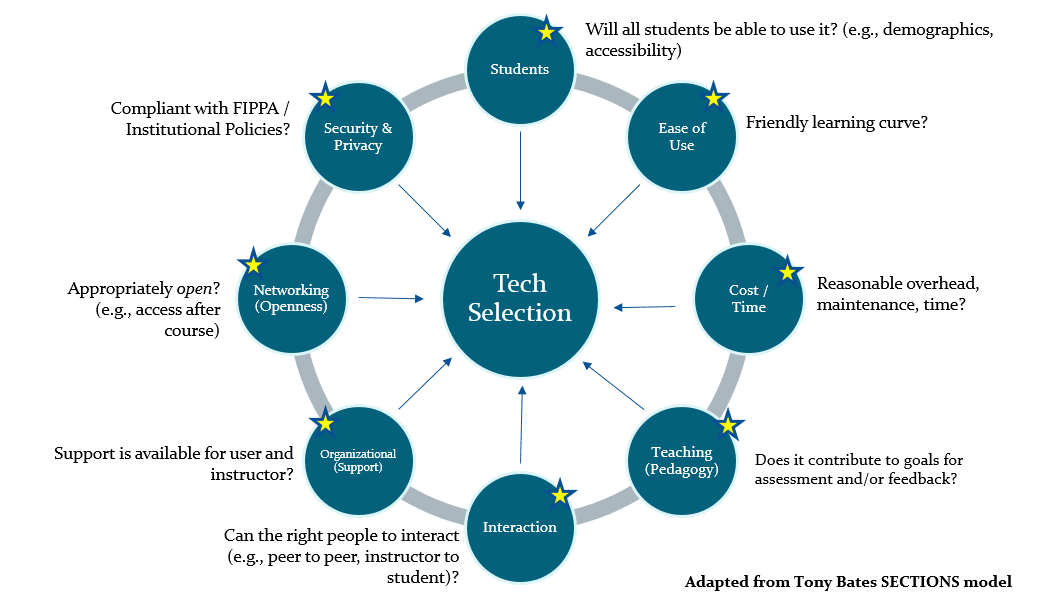
When using the SECTIONS model, the technology is assessed in various areas: students, ease of use, costs, teaching functions, interaction, an organizational issue, networking, security and privacy. By using this model to evaluate technology that the instructor picked, users will understand if the technology can be widely used in different learning content, easily understood and cost-effective.
Student
According to the SECTIONS model definition, when discussing the issue that related to students, the technology needs to widely fit different students, easy for students to access and have multiple options that allow students to choose based on their needs. VR and AR technology currently are exploring and expanding in many different areas. Extended reality use in medical practice has been explored by many researchers. Traditionally, most devices rely on 2D models to display information. With the introduction of XR, medical students can benefit from it to learn anatomy in the 3D way (Andrews, et.al., 2019). XR technology can also be used in the diagnosis and pre-procedural planning to support clinicians and researchers (Andrews, et.al., 2019). Since human-computer Interaction changed they way everyone interacts with computers, VR, AR can help student experience “in mixed-reality/virtual worlds are many and can result in effective, efficient and engaging learning” (Schneider, 2017). Student whoever can interact with these technologies can benefit from this new technology in learning.
Ease of Use
In one of the researches, student in the university by using the VR technology to simulate “how the enzymes behave under different conditions (Cai, et.al.,2018). Since AR technology is now implemented on some apps on the smartphone. There is a possibility to implement high-quality extended reality in easy to use and inexpensive devices. Although we still need more time to allow this new technology to be developed to a more stable phase. By look through how VR and AR technology grows fast in this age. There is a chance for extended technology to be used more widely.
Cost
Usually, new technology is always expensive. Based on the article “VR & AR Application Development cost explained”, the development of VR applications usually based on the content can cost from 10k to 70k. The development process on AR is a little bit lower, base on different content causes usually from 15k to 50k. However, as more and more company starts exploring various VR, AR products. The cost of these technologies is decreasing in recent years (Dede, Richard, 2017). Although the prices are cycling down for immersive media, currently it is still not affordable for each family but private high-end schools that can try XR in their school doing more research.
Teaching and media selection
Since there are not many XR implement in learning now, currently there is not much research on the comparison between XR learning and traditional learning. Based on Mayer’s principle in the multimedia design there are 12 principles that need to follow when design: Coherence, Signalling, Redundancy, Spatial contiguity, Temporal contiguity, Segmenting, Pre-training, Modality, Multimedia, Personalization, Voice, Image. By using XR, students usually experience a simulated environment that combines voice and image.
Interaction
There is one shortage when using VR, where when wearing VR helmet learning in a fully immersive environment. The instructor has lost the traditional face-to-face interaction. Therefore, the supporting technology in VR devices to capture user facial expression becomes an important function to help instructor understand their students (Liu, et.al., 2017). Since the XR combines the VR and AR technology, there is a possibility that in the future, students will wear simpler devices where allow student and instructor to keep the original interaction in class.
Organizational Issue
Due to the high cost for current XR technology, it is usually used within the school. Therefore, the use of XR must be provided by institutions. However, this actually has a benefit for users to use this technology in a more organized way. Usually, when the institution starts engaging technology, it will do an investigation to understand how the product can be used to benefit the overall teaching. And students can also get support from school if their class is involved with these new technologies.
Networking
The network in SECTIONS Model is to discuss if the technology can help with connecting students like social media. When student experiences in immersive technology, they can communicate within the same place but in the simulated environment.
Security and privacy
While technology grown supper fast, personal information security and privacy as one important topic that much is considered in use in Education. Especially in K-12 education, for students that are under-aged, how their user information et collection and being used must be tracked and consent in a meaningful way.
Conclusion
Also, XR technology is still new and still in development. However, I believe it can bring benefits to students in the future to learning from simulated experience that XR technology can enhance student’s learning.
Reference:
Andrews, C., Southworth, M. K., Silva, J. N. A., & Silva, J. R. (2019). Extended reality in medical practice. Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine, 21(4), 18. doi:10.1007/s11936-019-0722-7
Bates, A. W. (Tony). (2019b, October 10). Chapter 9: Choosing and using media in education: the SECTIONS model. Pressbooks.Bccampus.Ca; Tony Bates Associates Ltd. https://pressbooks.bccampus.ca/teachinginadigitalagev2/part/9-pedagogical-differences-between-media/
Cai, Y., van Joolingen, W., Walker, Z., & SpringerLink (Online service). (2018;). Virtual Reality Enzymes: An Interdisciplinary and International Project Towards an Inquiry-Based Pedagogy. In: Cai Y., van Joolingen W., Walker Z. (eds)VR, simulations and serious games for education. (45-54) Singapore: Springer Singapore. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-2844-2
Dede C.J., Richards J. (2017) Conclusion—Strategic Planning for R&D on Immersive Learning. In: Liu D., Dede C., Huang R., Richards J. (eds) Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Realities in Education. Smart Computing and Intelligence. Springer, Singapore
King, D., Tee, S., Falconer, L., Angell, C., Holley, D., & Mills, A. (2018). Virtual health education: Scaling practice to transform student learning: Using virtual reality learning environments in healthcare education to bridge the theory/practice gap and improve patient safety. Nurse Education Today, 71, 7-9. doi:10.1016/j.nedt.2018.08.002
Liu D., Bhagat K.K., Gao Y., Chang TW., Huang R. (2017) The Potentials and Trends of Virtual Reality in Education. In: Liu D., Dede C., Huang R., Richards J. (eds) Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Realities in Education. Smart Computing and Intelligence. Springer, Singapore
Najjar, R. (2020, February 17). Extended Reality (XR) explained through the 5 + 1 senses. Medium. https://uxdesign.cc/xr-through-5-1-senses-f396acf8a89f